Research subjects
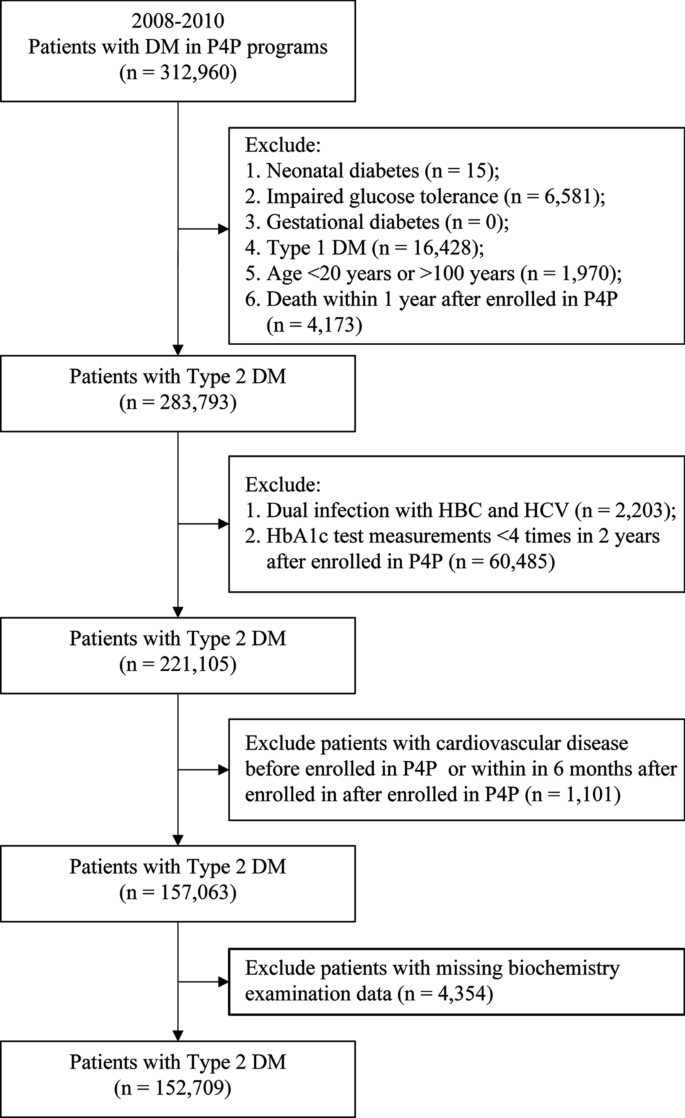
Patients with T2DM who joined the P4P from 2008 to 2010 were enrolled. Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of T2DM were defined as those who were hospitalized at least once or came in for outpatient visits at least three times within 1 year and had a primary or secondary diagnosis International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code “250,” “250.00,” or “250.02”38,39. Among them, patients with type 1 DM “250.x1” * or “250.x3;” gestational DM “648.0” or “648.8;” neonatal DM “775.1;” abnormal glucose tolerance test “790.2;” age < 20 years or > 100 years; and those who died within 1 year of joining P4P were excluded. Finally, 283,793 patients were included (Fig. 1). Based on the status of comorbid chronic hepatitis at enrollment, the patients were divided into four groups: no comorbid chronic hepatitis, named as “No chronic hepatitis”; comorbid liver B, named as “Hepatitis B” group; comorbid liver, named as “Hepatitis C” group; patients without viral hepatitis and with comorbid fatty liver were named as the “Fatty liver disease” group and were followed-up until the end of 2017. The “no comorbid chronic hepatitis” group was used as the reference group to analyze the correlation between different types of chronic hepatitis and the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Ethics statements
The National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) is derived from Taiwan’s mandatory National Health Insurance program was established by the National Health Insurance Administration Ministry of Health and Welfare and maintained by the National Health Research Institute (NHRI). The patient identifications in the National Health Insurance Research Database have been scrambled and de-identified by the Taiwan government, and the database is commonly used for different types of research such as in medical, and public health fields. Thus, informed consent was waived by the Research Ethics Committee of the China Medical University, and the study protocol was approved by the research ethics committee of China Medical University and Hospital (IRB number: CMUH106-REC3-153) and was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Data sources
This retrospective cohort study analyzed data from the National Health Insurance Research Database of the “Applied Health Research Data Integration Service from National Health Insurance Administration”. The data included outpatient prescriptions and treatments, outpatient prescriptions and medical orders, inpatient medical expense lists, inpatient medical expense and medical order lists, insurance details of persons, major injury and illness, medical institution master files, diagnosis, and P4P education records.
Definitions of variables
Hepatitis B: Those with ICD-9 070.2, 070.20, 070.21, 070.22, 070.23, 070.3070.31, 070.32, or 070.33 or ICD-10 B16, B17.0, B18.0, B18.1, or B19.1 as the primary and secondary diagnosis during two outpatient visits or one hospitalization within 365 days of study enrollment.
Hepatitis C: Those with ICD-9 070.41, 070.44, 070.51, or V02.62 or ICD-10 B17.10, B17.11, B18.2, B19.20, B19.21, or Z22.52 as the primary and secondary diagnosis during two outpatient visits or one hospitalization within 365 days of study enrollment.
NAFLD: Those with ICD-9 571.8, 571.9, or ICD-10 K74.4, K74.5, K74.60, K74.69, K76.0, K76.9, etc. as the primary and secondary diagnosis during two outpatient visits or one hospitalization within 365 days of study enrollment, and without the occurrence of a hepatitis B or C code, for whom the first hospital visit within 365 days was defined as the date of diagnosis. Patients with concurrent viral hepatitis and NAFLD were classified as having viral hepatitis.
Age-based categorization included 20–39, 40–54, 55–64, 65–74, and ≥ 75 years age groups. Monthly salary was divided into five grades, namely ≤ NTD 17,280, NTD 17,281–22,800, NTD 22,801–36,300, NTD 36,301–45,800, and ≥ NTD 45,801. Charlson comorbidity index was divided into 0, 1, 2, and ≥ 3 after excluding scores correlated with independent or dependent variables40.
The diabetes complications severity index (DCSI) was scored as 0, 1, and ≥ 2 points. The DCSI was calculated based on the classification and scoring method proposed by Young et al. If the patient had no complication, the score would be 0; for each complication, 1 point would be added; if the complication was serious, 2 points would be added. Based on this calculation method, the maximum score was 13 points41.
Cardiovascular disease: Those with ICD-9 398.91, 402.xx, 404.xx, 410.xx–414.xx, 422.xx, 425.xx or 428.xx, or ICD-10 I09.81, I11, I13, I20–I22, I24, I25, I40–I43, I50, R09.89, etc. as the primary and secondary diagnosis during two outpatient visits or one hospitalization within 365 days of study enrollment42.
Calculation of the coefficient of variation (CV% = standard deviation/mean) of HbA1c and fasting blood glucose: All measurements in the first year were used, and if the measurements were taken less than four times in the first year, measurements taken up to the second year were included. If measurements were taken less than four times in the 2 years, the patient would be excluded.
Adjusted CV = CV/√ (n/n − 1): When the examination data were limited, the examination times would affect the result of the CV. In this case, a relatively correct result of the CV with a reduced effect of the examination times could be obtained by correcting the examination times.
Analytical methods
Descriptive and inferential statistics were carried out according to the research objectives and framework. All research tests were based on a significance level of α = 0.05, and all statistical analyses were conducted using SAS software for Windows, version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Descriptive statistics such as frequency, percentage, average, and standard deviation were used to describe the dependent and independent variables to be investigated in this study. This study adopted descriptive statistics to present the demographic characteristics, status of comorbidities, blood biochemical indicators, health status, economic factors, and medical care provider characteristics of patients with diabetes. The incidence of cardiovascular disease in patients with T2DM with chronic hepatitis per 1000 person-years was tested using univariate Poisson regression. The relative risks of cardiovascular disease in the four groups were calculated using a Cox proportional hazards model.